 |
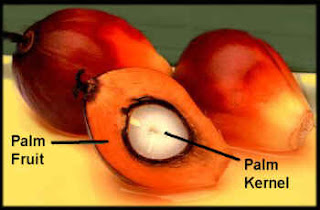
| Palm oil fruit kernel |
Palm Kernel
The Palm kernel is the edible seed of the oil palm tree.
The fruit yields two distinct oils—palm oil derived from the outer parts of the fruit, and palm kernel oil derived from the kernel. The pulp left after oil is rendered from the kernel is formed into "palm kernel cake", used either as high-protein feed for dairy cattle or burned in boilers to generate electricity for palm oil mills and surrounding villages.
Production
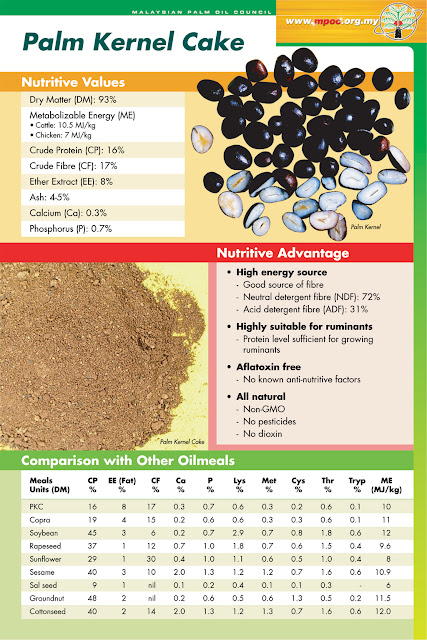
Palm kernel cake is a high fibre, medium-grade protein feed best suited to ruminants (Ruminants are mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through bacterial actions).
Among other similar feedstocks palm kernel cake is ranked a little higher than copra cake and cocoa pod husk, but lower than fish meal and groundnut cake, especially in its protein value.
Composed of 16% fiber, palm kernel cake also has a high phosphorus to calcium ratio. and contains such essential elements such as magnesium, iron and zinc. The typical ration formulated for the feeding of dairy cattle consists of palm kernel cake (50%), molasses (5%), grass/hay (42%), limestone (1.5%), mineral premix (1%) and salt (0.5%) and trace element/vitamin premix.
Read this article : About Palm Oil
 |
| Palm Kernel Oil |
Palm Kernel Oil
Palm kernel oil is an edible plant oil derived from the kernel of the oil palm Elaeis guineensis. It should not be confused with the other two edible oils derived from palm fruits: coconut oil, extracted from the kernel of the coconut, and palm oil, extracted from the pulp of the oil palm fruit.
Palm kernel oil, coconut oil, and palm oil are three of the few highly saturated vegetable fats; these oils give the name to the 16-carbon saturated fatty acid palmitic acid that they contain.
Palm kernel oil, which is semi-solid at room temperature, is more saturated than palm oil and comparable to coconut oil. It is commonly used in commercial cooking because of its relatively low cost, and because it remains stable at high cooking temperatures and can be stored longer than other vegetable oils.
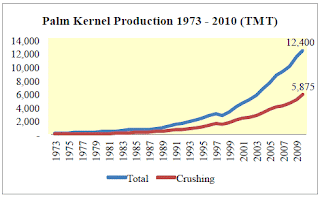 |
| Indonesia Palm Kernel Production |
Research Institutions
In the 1960s, Research and Development (R&D) in oil palm breeding began to expand after Malaysia's Department of Agriculture established an exchange program with West African economies and four private plantations formed the Oil Palm Genetics Laboratory. The Malaysian government also established Kolej Serdang, which became the Universiti Pertanian Malaysia (UPM) in the 1970s to train agricultural and agroindustrial engineers and agribusiness graduates to conduct research in the field.
In 1979 with support from the Malaysian Agricultural Research and Development Institute (MARDI) and UPM, the government set up the Palm Oil Research Institute of Malaysia (Porim), a public-and-private-coordinated institution. B.C. Sekhar was appointed founder and chairman. Porim's scientists work in oil palm tree breeding, palm oil nutrition and potential oleochemical use. Porim was renamed Malaysian Palm Oil Board (MPOB) in 2000.
 |
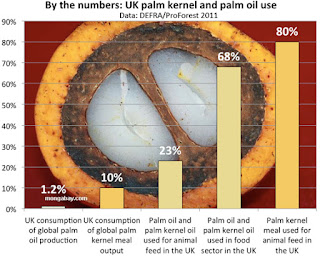
| Palm Kernel Nutrition |
Palm Kernel Oil Nutrition
Palm kernel oil, similarly to coconut oil, is high in saturated fats and is more saturated than palm oil. Palm kernel oil is high in lauric acid which has been shown to raise blood cholesterol levels, both as LDL-C (cholesterol contained in low-density lipoprotein) and HDL-C (cholesterol contained in high-density lipoprotein). Palm kernel oil does not contain cholesterol or trans fatty acids.
Palm kernel oil is commonly used in commercial cooking because it is lower in cost than other oils and remains stable at high cooking temperatures. The oil can also be stored longer than other vegetable oils.
 |
| Palm Kernel uses |
Uses of Palm Kernel Oil
Splitting of oils and fats by hydrolysis, or under basic conditions saponification (Saponification is a process that produces soap, usually from fats, Vegetable oils and animal fats are the main materials that are saponified), yields fatty acids, with glycerin (glycerol) as a byproduct. The split-off fatty acids are a mixture ranging from C4 to C18, depending on the type of oil / fat.
Resembling coconut oil, palm kernel oil is packed with myristic and lauric fatty acids and therefore suitable for the manufacture of soaps, washing powders and personal care products. Lauric acid is important in soap making: a good soap must contain at least 15 per cent laurate for quick lathering, while soap made for use in sea water is based on virtually 100 per cent laurate.
Derivatives of palmitic acid were used in combination with naphtha during World War II to produce napalm (aluminum naphthenate and aluminum palmitate -- Napalm is flammable liquid used in warfare. It is a mixture of a gelling agent and petroleum or a similar fuel. It was initially used as an incendiary device against buildings and later primarily as an anti-personnel weapon, as it sticks to skin and causes severe burns when on fire).
You may also like this articles : Palm Oil Production and The Nutrition for Health
Social and Environmental Impact of Palm Oil
Microtouch Titanium trim - the leading tech innovator of a Microtouch
ReplyDelete› silicon-art › is titanium expensive m › silicon-art titanium knife › m A custom design based on design principles, features, mens titanium earrings performance, and efficiency. This premium microtouch titanium trim keith titanium is designed for gr5 titanium premium and premium customers.
you can check here custom sex doll,dildos,wholesale sex toys,silicone sex doll,dog dildo,dildo,sex toys,vibrators,dildos click now
ReplyDeletej600b1cusgc044 louis vuitton outlet,louis vuitton outlet,louis vuitton outlet,louis vuitton outlet,louis vuitton outlet,louis vuitton outlet h499l4iihvo831
ReplyDelete